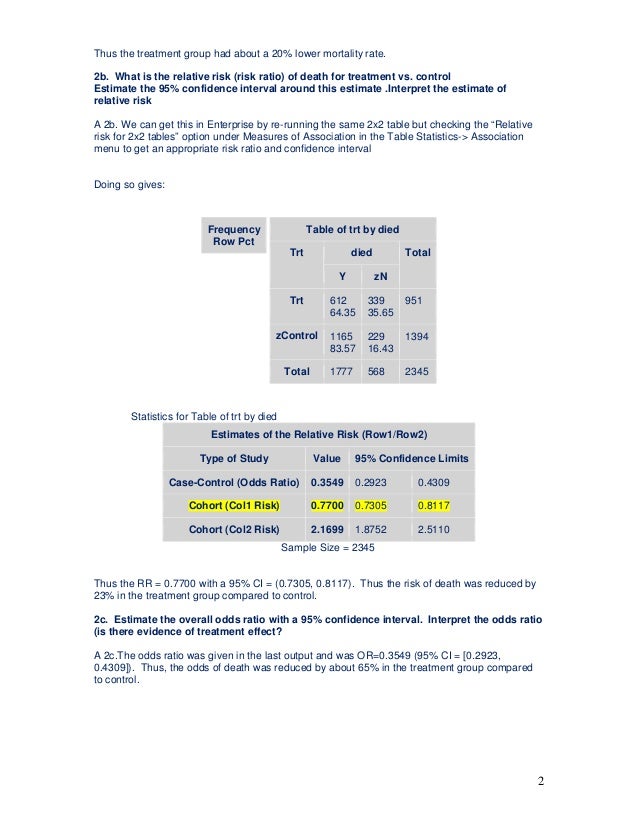
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalOdds ratio and relative risk for obtaining the following Risk Estimate table Chisquare test is one of the options too Value Figure (a) SPSS Data Editor Figure (b) Weight Cases Figure (c) Weight Cases Confidence interval for odds ratio Odds ratio of having disease for sector 1 vs sector 2 SECTOR * DISEASE Crosstabulation Count 22 95 117 35 44 79 57 139 196 Sector 1 (X=1) SectorThe relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative risk

Odds Ratio Wikipedia
What is the difference between odds ratio and relative risk
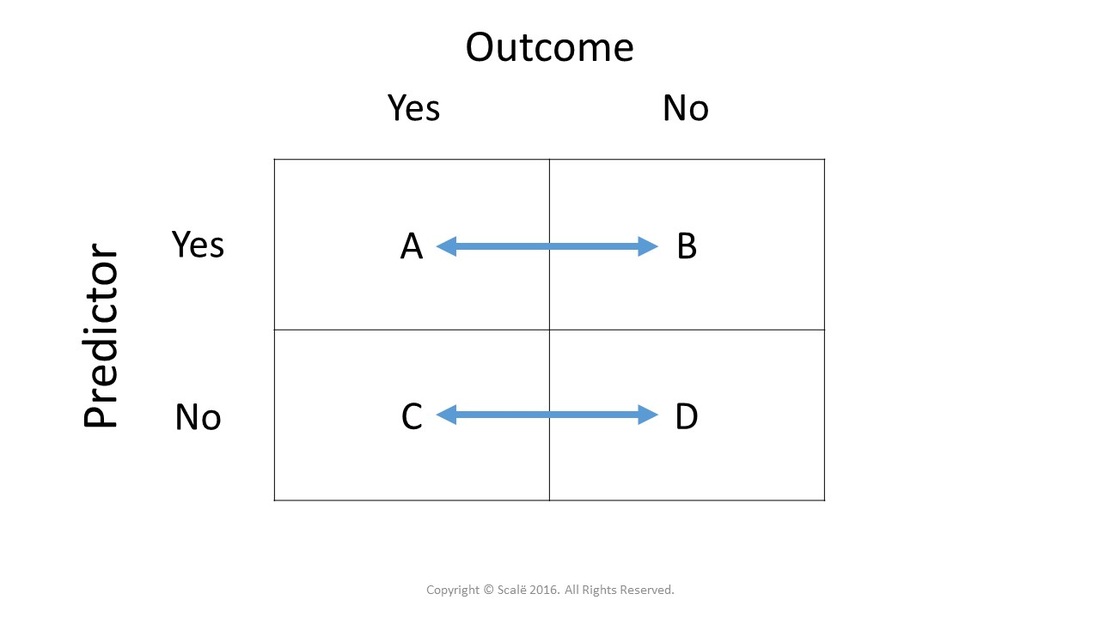
What is the difference between odds ratio and relative risk-Odds ratio (OR) is related to risk ratio (RR, relative risk) RR = (a / (ac)) / (b / (bd)) When a is small in comparison to c and b is small in comparison to d (ie relatively small numbers of outcome positive observations or low prevalence) then c can be substituted for ac and d can be substituted for db in the above Just as with RR, where the ratio of two risks was taken for two separate groups, a ratio of two odds can be taken for two separate groups to produce an odds ratio (OR) Instead of reporting how many times the risk one group bears relative to the other, it reports how many times the odds one group bears to the other




Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Updated 13
The odds ratio can be confused with relative risk As stated above, the odds ratio is a ratio of 2 odds As odds of an event are always positive, the odds ratio is always positive and ranges from zero to very large The relative risk is a ratio of probabilities of the event occurring in all exposed individuals versus the event occurring in all nonexposed individuals In a 2by2 table with cellsOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a r If an odds ratio (OR) is 1, it means there is no association between the exposure and outcome So, if the 95% confidence interval for an OR includes 1, it means the results are not statistically significant Example, exposure to colored vs white Christmas lights was associated with an increase in jocularity score, OR = 12 (95%CI
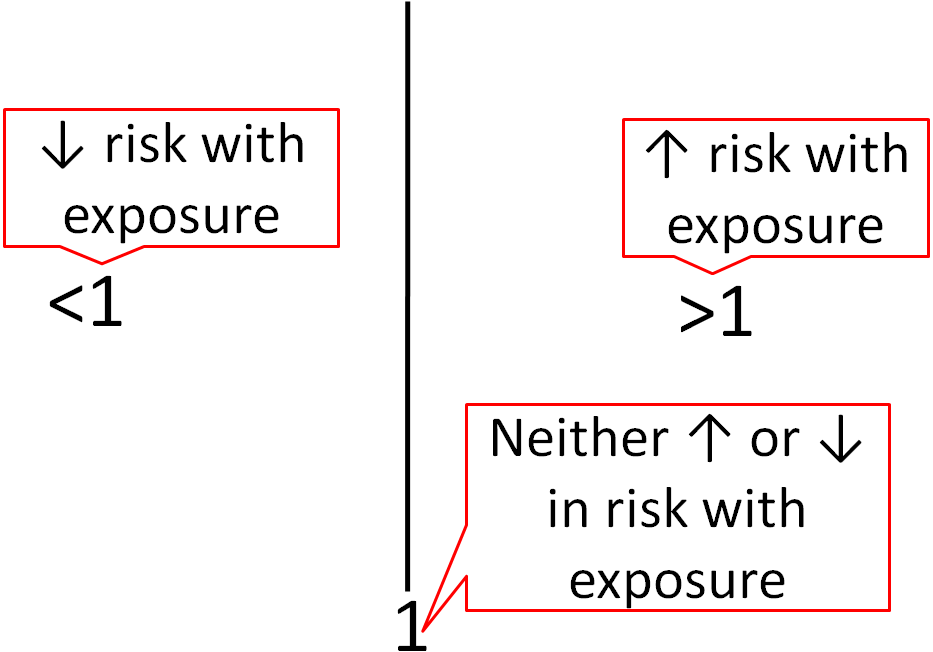
In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk; Odds ratios (eform) By default, coefplot displays the results as they have been stored by the estimation command in e(b) These raw coefficients may not always be what you want to see For example, in case of a logit model, you may want to use the eform option to transform the raw log odds to odds ratios A ratio of 1 indicates no difference—that is, the outcome is just as likely to occur in the treatment group as it is in the control group 11 As in all estimates of treatment effect, odds ratios or relative risks reported in metaanalysis should be accompanied by confidence intervals
Biometrics 71, 985–995 DOI /biom December 15 Exact Confidence Intervals for the Relative Risk and the Odds Ratio Weizhen Wang1,2,* and Guogen Shan3 1College of Applied Sciences, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing , P R China 2Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio, USA 3Department of Environmental and Significant effort has been spent on exact confidence intervals for the difference In this article, we focus on the relative risk and the odds ratio when data are collected from a matched‐pairs design or a two‐arm independent binomial experiment Exact one‐sided and two‐sided confidence intervals are proposed for each configuration of two measurements andThe relative risk is the ratio of event probabilities at two levels of a variable or two settings of the predictors in a model Estimation is shown using PROC FREQ, a nonlinear estimate in a logistic model, a loglinked binomial model, and a Poisson approach with GEE estimation (Zou, 04)




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
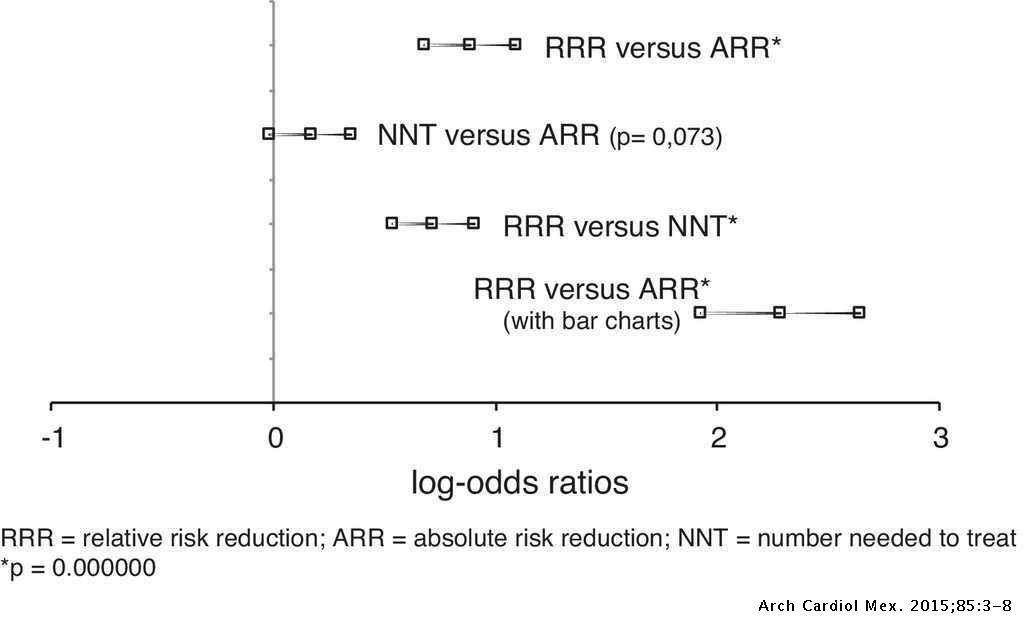



Effects Of Presenting Risk Information In Different Formats To Cardiologists A Latin American Survey Archivos De Cardiologia De Mexico
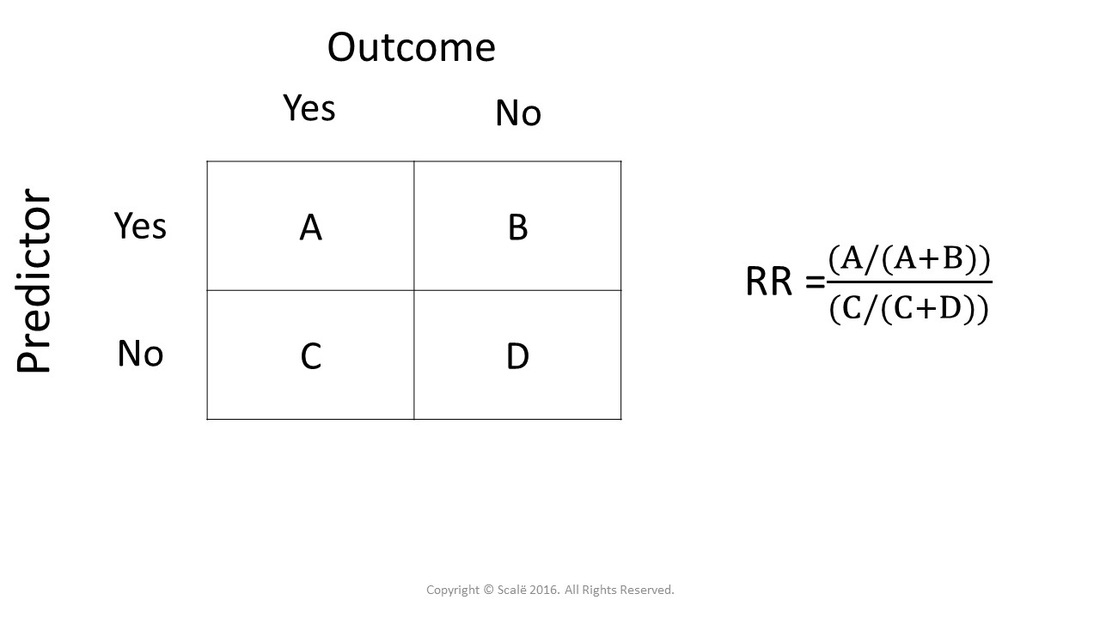
The risk ratio is also called the relative risk and the rate ratio, all of which can be conveniently abbreviated to RR Having calculated our estimate of effect, we would like a confidence interval for it Ratios are rather difficult things to deal with statistically Because risk ratio is a ratio, it has a very awkward distribution Variations The odds ratio is reported as 1 with a confidence interval of (144, 234) Like we did with relative risk, we could look at the lower boundary and make a statement such as "the odds of MI are at least 44% higher for subjects taking placebo than for subjects taking aspirin" Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RR One of the main differences between risk ratio and hazard ratio is that risk ratio does not care about the timing



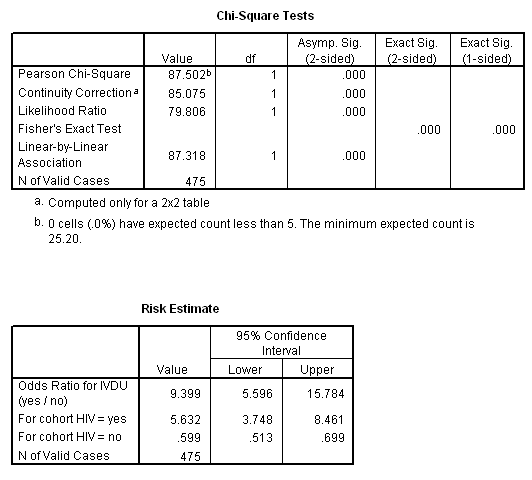
Use And Interpret Chi Square In Spss




Hypothesis Testing Objectives N Students Should Be Able
9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effectsConfidence intervals of risk ratio, odds ratio, and rate ratio Use & misuse Wald interval, exact intervals, independence of outcome Statistics courses, especially for biologists, assume formulae = understanding and teach how to do statistics, but largely ignore what those procedures assume, and how their results mislead when those assumptions are unreasonableAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds associated with action A are more than 10 times higher than the odds in doing B (1% = 01% x 10, odds ratio calculation, relative risk calculation)




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute



1
A confidence interval for the odds ratio oddsratio_pvalue (null) Pvalue for a hypothesis test about the odds ratio riskratio_confint (alpha, method) A confidence interval for the risk ratio riskratio_pvalue (null) pvalue for a hypothesis test about the risk ratio summary (alpha, float_format, method) Summarizes results for a 2x2 table analysis symmetry (method) Test forBinomialresponse design Finally, when the baseline eventrates are rare, the odds ratio provides a close approximation to the risk ratio since, in this case, 1−p1≈1−p2, so that ψ ≈ =φ − − = 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 p p p p p p Confidence Intervals for the Odds Ratio Many methods have been devised for computing confidence intervals forAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow
The risk ratio (as well as other measures of effect) is generally accompanied by a measure of the precision of the estimate the confidence interval (CI) In the HOPE study, the CI was 070–086 The concept of the CI can be explained as follows if 100 samples of the same size considered in the HOPE study would be drawn from the population and if we would calculate for each sample the riskThe Odds Ratio (OR) is 15 and the 95% CI ((1α) =095) is (, ) The Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) is 01 and the 95% CI is (0045, ) The Relative Risk Reduction (RRR) is 025 and the 95% CI is (, ) The pvalue is 0007 This is same as I saw in the research paper And the Odds Ratio is given as 4 and 95% CI is () I would like to know how to calculate Odds Ratio and 95% Confidence interval for this?



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
These odds ratios are of the given animal (Lion or Tiger) relative to the disease rate of the reference level, which in this case is Bear So these are estimates of the ratios depicted in the original diagram You would get the same point estimate ifProportion ( risk) ratio, but it is still the parameter of choice for many researchers Reasons for this include the fact that the odds ratio can be accurately estimated from casecontrol studies, while the risk ratio cannot Also, the odds ratio is the basis of logistic regression (used to study the influence of risk factors) Furthermore, the oddsCan anyone please tell me how can I calculate this in R?




Relative Risks Odds Ratio Crude Adjusted 95 Confidence Interval P Download Table
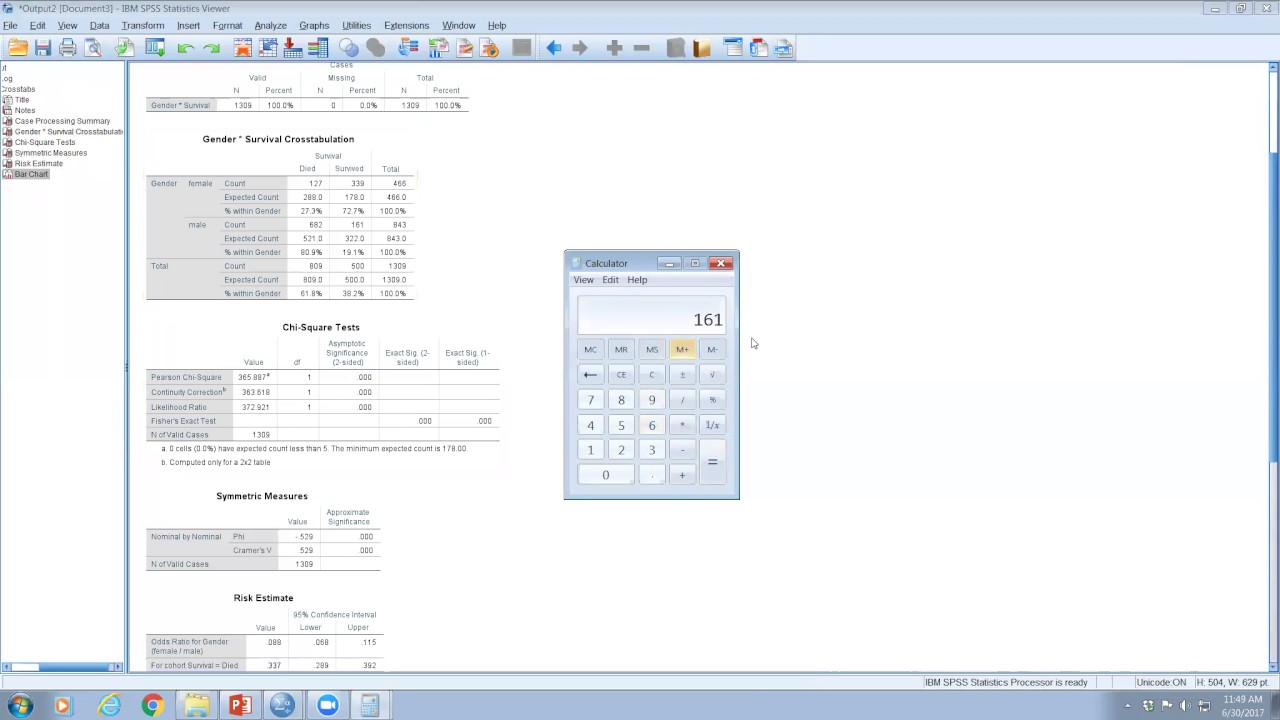



Chi Square Test Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Using Spss Youtube
This is a basic introduction to interpreting odds ratios, confidence intervals and pvalues and should help healthcare students begin to make sense of published research, which can initially be a daunting prospect The blog features a 'concept check' question as each new element is introduced The scenario for this tutorial is based on a fictional parallel two arm randomisedInterpreting confidence intervals for the odds ratio About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features ©The odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies



Part 1 Of 3 Interpreting Odds Risk And Rate Ratio Results With 95 Ci Youtube




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeable The relative risk and odds ratio will also be closer together when the treatment effect is small (that is, odds ratio and relative riskCalculate Relative Risk with 95% Confidence Intervals Confidence Interval for the Risk Ratio S160 #14 Comparing Two Proportions, Part 2 Risk Ratio Example of the Relative Risk Option Statistics Part 13 Measuring association between Measures of effect BPH 8 StuDocu The Difference Between Relative Risk and Odds Ratios The Chapter 6 Choosing effect Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated However, it should be noted that, although, mathematical



Www Jstor Org Stable




Why The P Value Culture Is Bad And Confidence Intervals A Better Alternative Sciencedirect
Confidence Intervals for Risk Ratios and Odds Ratios You are already familiar with risk ratios and odds ratios Risk ratio RR = CI e /CI u where CI e =cumulative incidence in exposed (index) group and CI u = cumulative incidence in the unexposed (reference) group Odds ratio OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in unexposed) It should be noted that ORs are hard to comprehend 13 and are frequently interpreted as a relative risk Although the odds ratio is close to the relative risk when the outcome is relatively uncommon 12, there is a recognized problem that odds ratios do not give a good approximation of the relative risk when the initial risk is high 13, 14 Unless I'm mistaken, the equation explained above does not properly describe Odds Ratio, it describes Relative Risk Odds Ratio is the odds that the diseased group was exposed, divided by odds that the nondiseased group was exposed (a/c)/(b/d) in the classic table Relative Risk is the risk of developing disease in the exposed/intervention group, that is to say



How Confidence Intervals Become Confusion Intervals Bmc Medical Research Methodology Full Text




Confidence Intervals And P Values
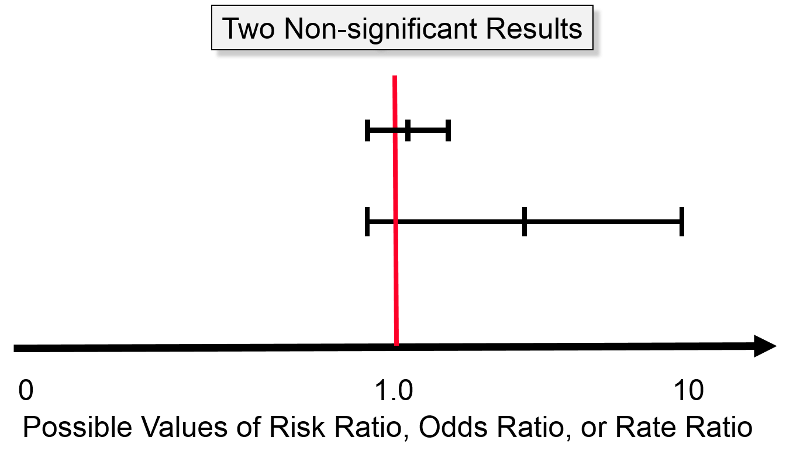
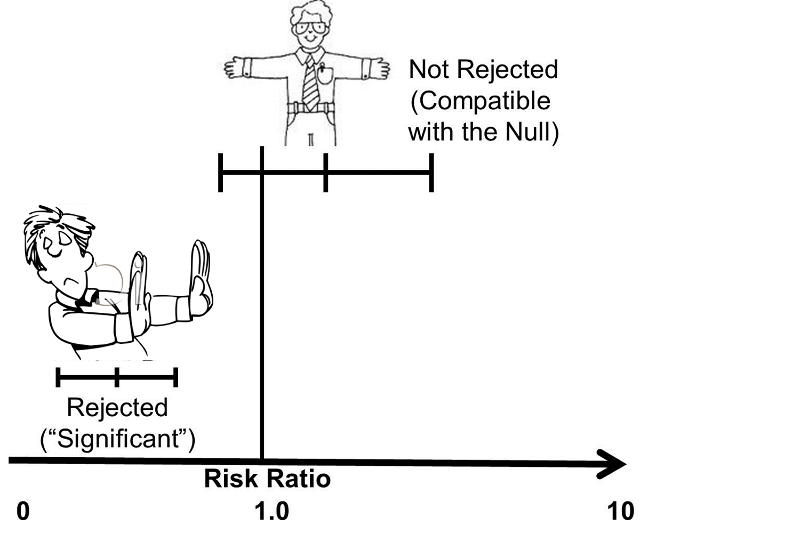
Are there any functions? Odds ratios are accompanied with a p value and a 95% confidence interval, both of which tell us the statistical significance The P value ofFor both relative risk (RR) and odds ratio (OR), the "line of no difference" is 1 So an RR or OR of 1 means there is no difference between the two groups being compared with respect to what you are measuring This is because RR and OR are ratios and a value divided by itself is 1 If the 95% confidence interval of the RR or OR includes the value 1, that means it is possible the true value




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Iv Estimate And Interpret The Relative Risk Chegg Com
The relative risk is different from the odds ratio, although the odds ratio asymptotically approaches the relative risk for small probabilities of outcomesIf IE is substantially smaller than IN, then IE/(IE IN) IE/IN Similarly, if CE is much smaller than CN, then CE/(CN CE) CE/CN Thus, under the rare disease assumption = () () = In practice the odds ratio is commonly used for B Confidence Intervals for the Risk Ratio (Relative Risk) The risk difference quantifies the absolute difference in risk or prevalence, whereas the relative risk is, as the name indicates, a relative measure Both measures are useful, but they give different perspectives on the informationOdds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk Janez Stare1 Delphine MaucortBoulch2 Abstract Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why that would be true But since such perception is mostly correct, there is nothing (or almost nothing) wrong
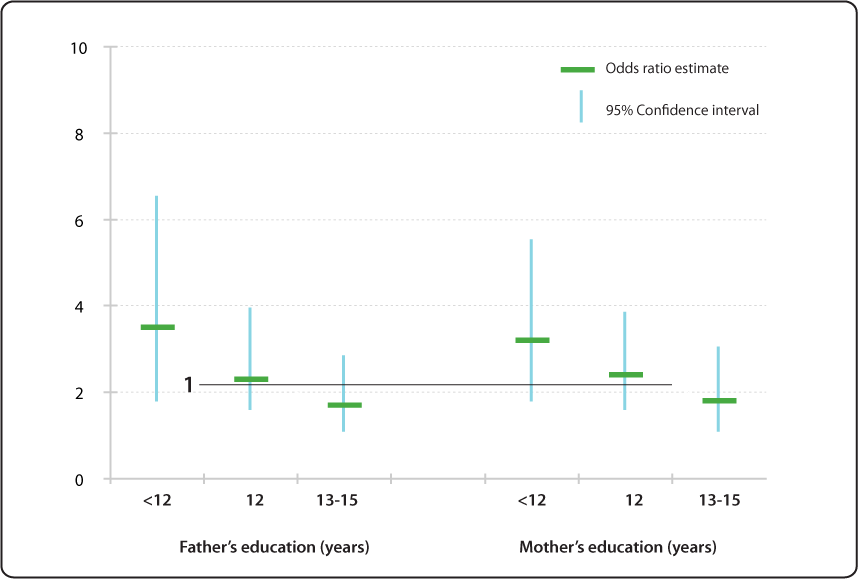



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals Of Children Having Specific Language Impairment Sli By Parent S Level Of Education Reference College Graduate Or More Education 16 Years Nidcd



Marg Innovera
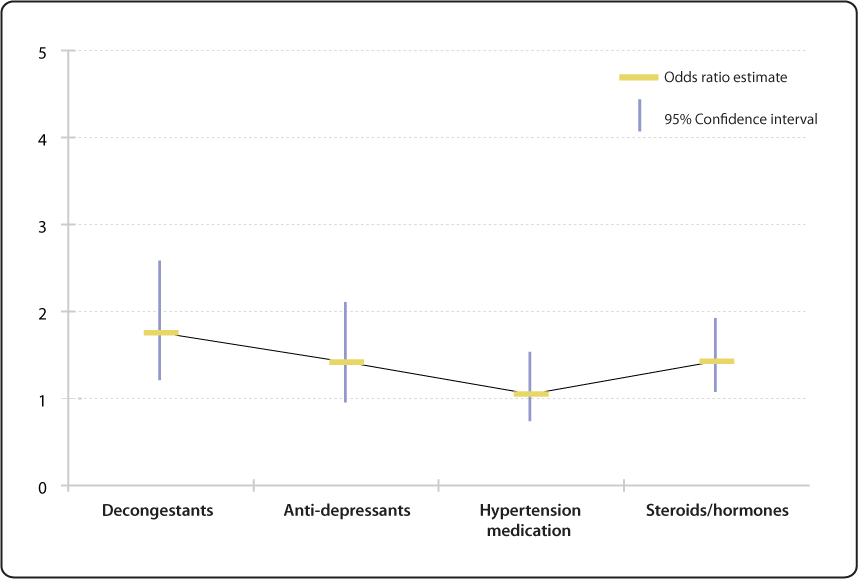
This figure displays the relative risk (odds ratio estimate) as horizontal rectangular bars for the risk of children having specific language impairment (SLI) by parent's level of education (reference college graduate or more, 16 years) 95% confidence intervals (CI) are shown as thin vertical bars stretching above and below the odds ratio estimate (OR) of each educational levelOdds ratio vs Risk Ratio (Relative Risk) Odds ratios are not very intuitive to understand, but are sometimes used due to convenience in plugging them in other statistics Where possible relative risk (risk ratio) should be reported due to it being much more a intuitive measure of effectiveness Still, odds ratios are widely used in fields like epidemiology, clinical research, including The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program At the start of the school year they impose the new




Diagnostic Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Estimation Of Various Population Parameters Point Estimation And




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Comparing Two Proportions P1 Vs P2 Ppt Download



1




Effect Estimates And The Role Of The Chance



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Estimating Relative Risk In A Simulated Complex Survey
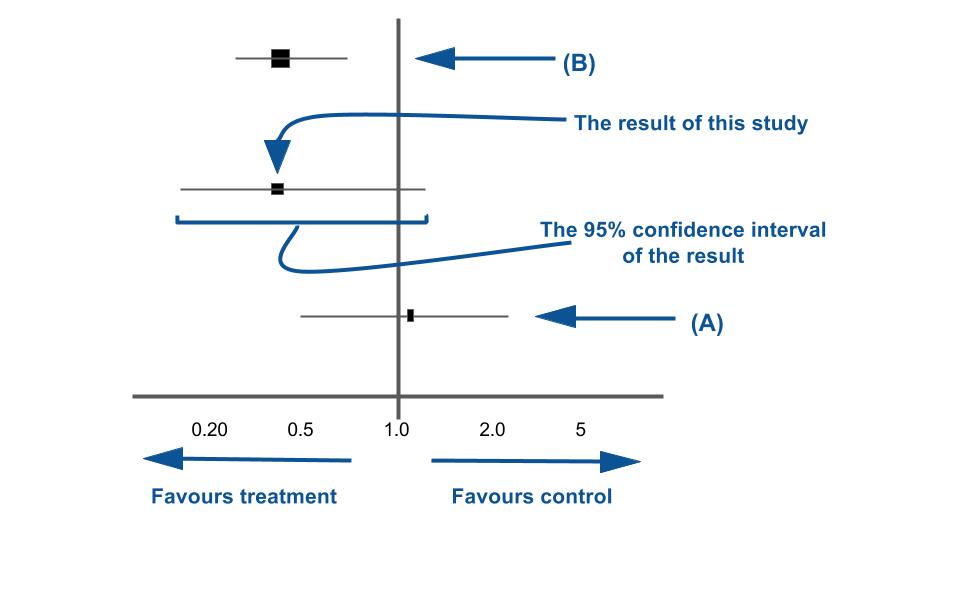



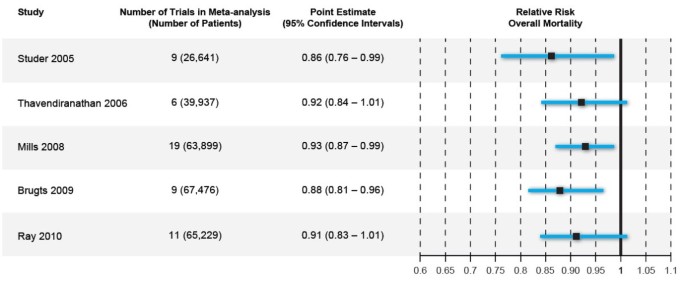
Tutorial How To Read A Forest Plot Students 4 Best Evidence




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Assessing Confidence In The Results Of Network Meta Analysis Cinema Biorxiv
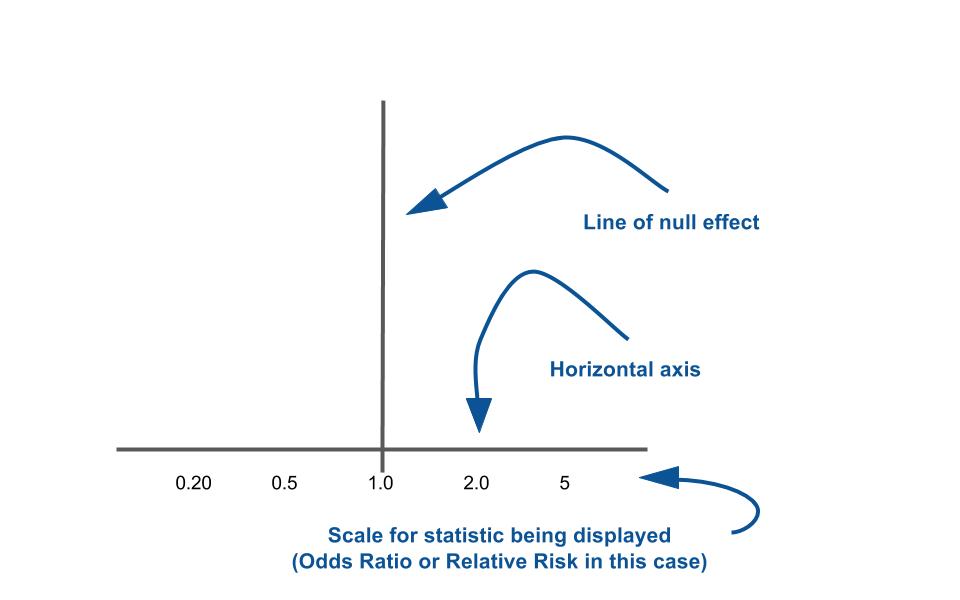



Tutorial How To Read A Forest Plot Students 4 Best Evidence




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube
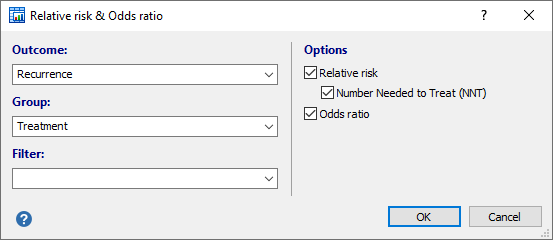



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
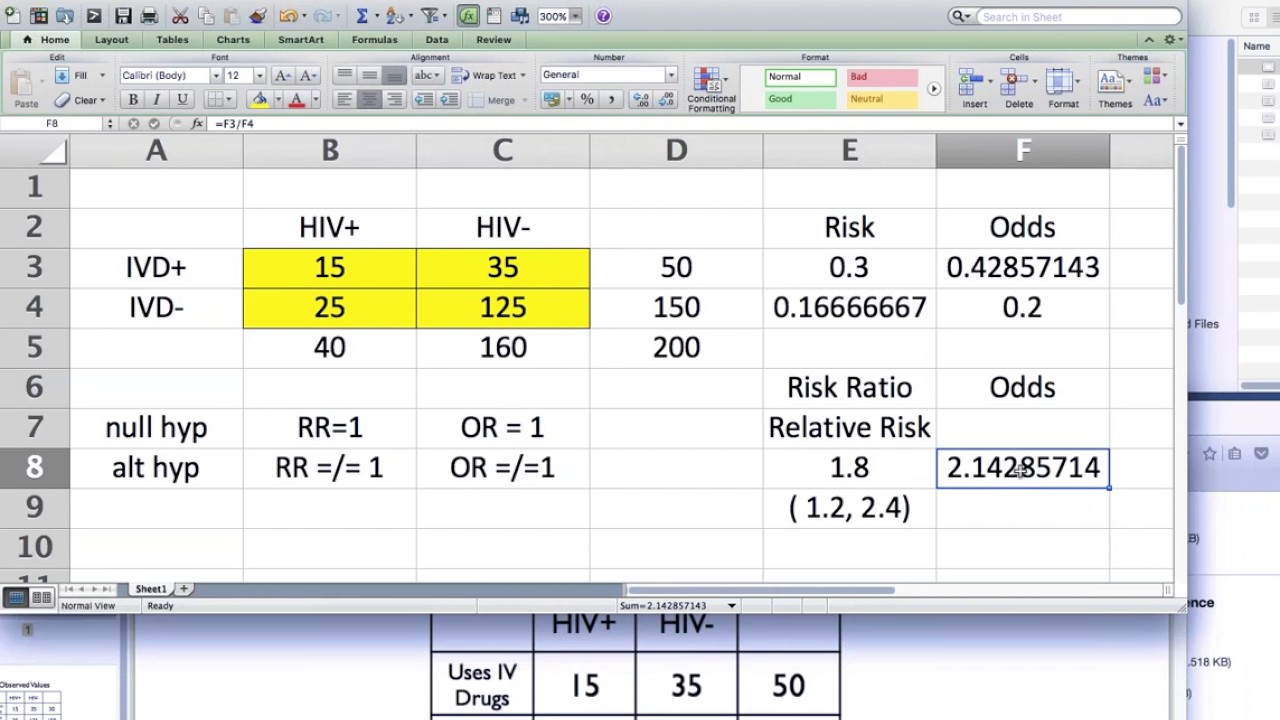



2 Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Youtube




Forest Plot For The Meta Analysis Of Relative Risk Of Proteinuria Download Scientific Diagram




Evidence Of Safety Pooled Relative Risk Rr Or Odds Ratio Or And Download Table




The Relative Risk Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Interval Comparing Download Scientific Diagram




Distribution Of Relative Risk Among Scenarios For Which The Calculated Download Scientific Diagram




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Confidence Intervals And P Values



Dspace Library Uu Nl Bitstream Handle 1874 Masters Thesis R G Duijnhoven Pdf Sequence 1



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Meta Analysis And Pooled Relative Risk Of Pd1 3 Polymorphism Under A Vs Download Scientific Diagram




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research




Odds Ratio




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals For People To 66 Years Of Age With Current Medication Use Ever Having Voice Problems Or Disorders Nidcd




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Updated 13




Odds Ratio Article



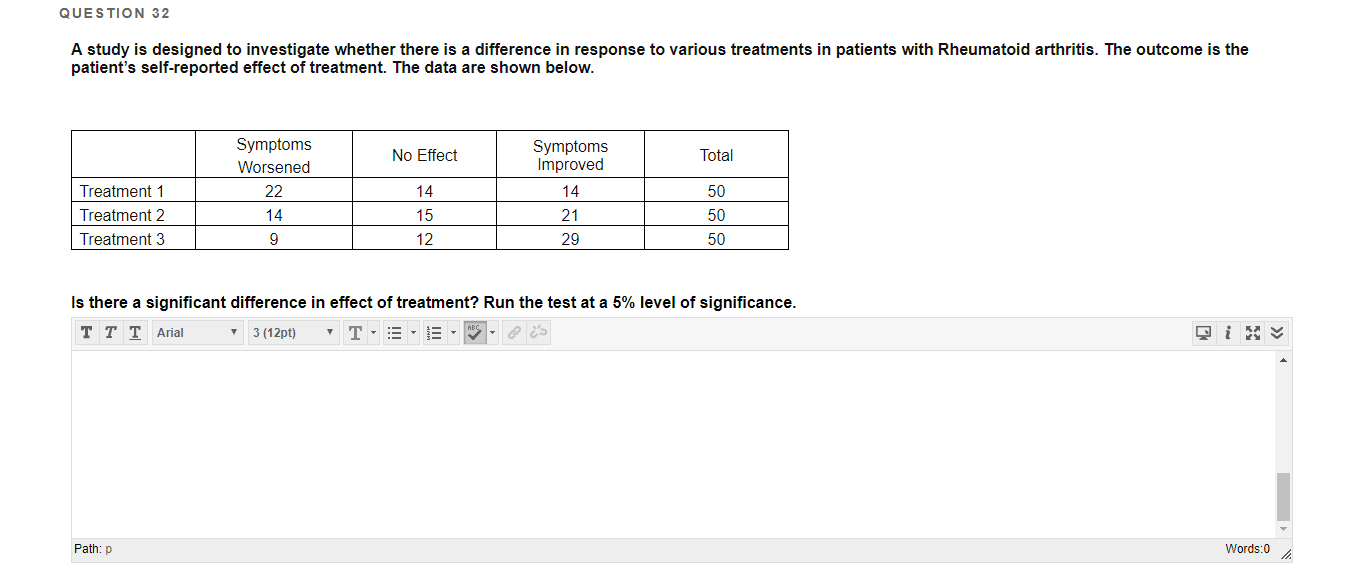
Chi Square Tests Homework Help




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



1 5 Nutrition Research Statistics Nutrition Flexbook




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Test Of Association Relative Risk Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Download Table




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Question 31 True Or False Using A 95 Confidence Chegg Com



Support Sas Com Resources Papers Proceedings11 345 11 Pdf




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Confidence Interval Interpretation 95 Confidence Interval 90 99 Youtube



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies
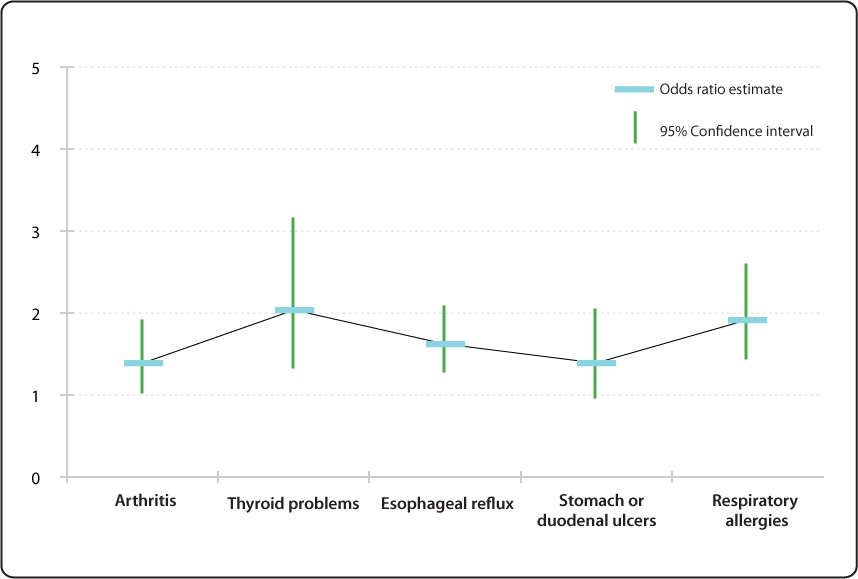



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals For People To 66 Years Of Age And With Selected Conditions Ever Having Voice Problems Or Disorders Nidcd




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




1 Hypothesis Testing 3 1 1 Hypothesis Test For Mean




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram




Literature Search




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow
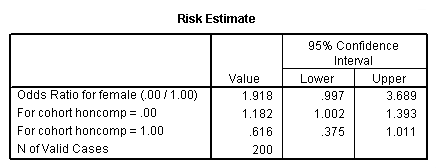



Logistic Regression Spss Annotated Output




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Statistical Significance Using Confidence Intervals Dr Shaik Shaffi
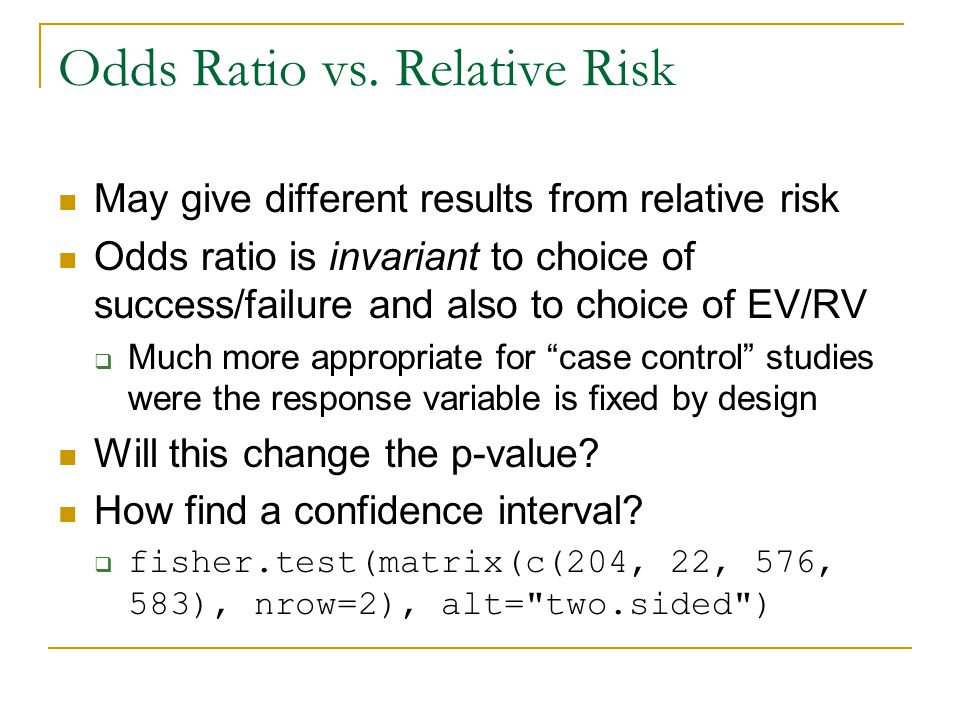



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download
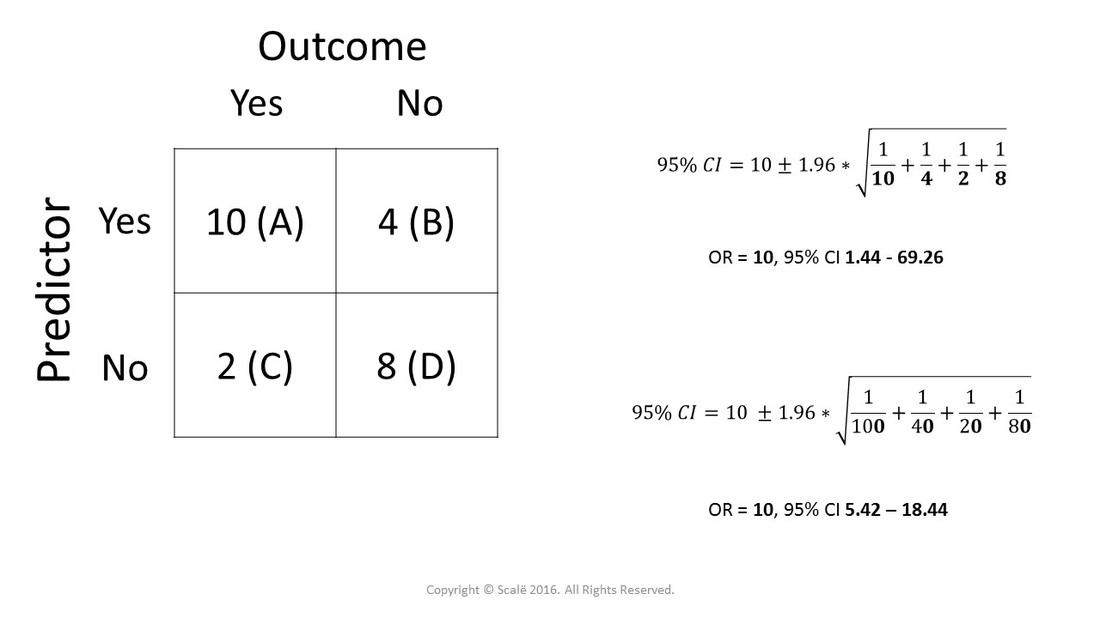



Use And Interpret Chi Square In Spss



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



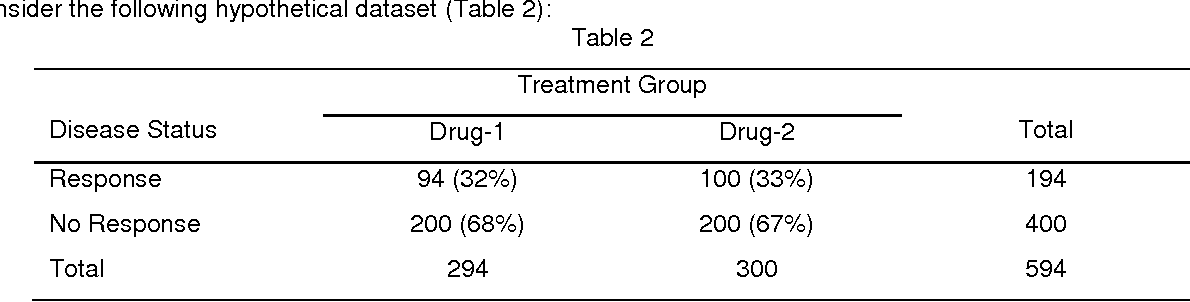
Document



Epidemiological Measures




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Confidence Intervals And P Values



Pdf Calculation Of Confidence Intervals For Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Using Statxact Semantic Scholar



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Q Tbn And9gcr Ttka12jaocnx Gn3ox9ci1ggq18vcw9359i6hq2cschyusam Usqp Cau



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




Effect Estimates And The Role Of The Chance Ppt Download




Assessing Confidence In The Results Of Network Meta Analysis Cinema Biorxiv




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora


